Solution Verified by Toppr Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1 The work done on an object does not depend on the : (a) displacement (b) angle between force and displacement (c) force applied (d) initial velocity of the object View Solution Q Refer question no 12 in the chapter 11.
Introduction to College Physics I: An Exploration of Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids, and Modern Physics | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Heat
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d = (2.00 m)i + (4.00 m)j – (3.00 m)k, its velocity is v = – (3.58 m/s)i + (6.72 m/s)j + (8.96 m/s)k and it

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
. Find (a) the acceleration of the object, (b) the angular momentum of the object about the origin, (c) the torque about the origin acting on the object, and (d) the angle between the velocity of the object and the force acting on the object. How do we benefit from the production of vitamin K by microbes?

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
SOLVED: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d→ = (2.00 m) î + (4.00 m) ĵ – (3.00 m) k̂ , its velocity At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d = (2.00 m)i + (4.00 m)j – (3.00 m)k, its velocity is v = (6.99 m/s)i + (3.66 m/s)j + (8.14 m/s)k and it is subject to a force F = (9.02 N)i – (3.34 N)j + (9.52 N)k.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
At The Instant The Displacement Of A 2.00kg
At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d = (2.00 m)i + (4.00 m)j – (3.00 m)k, its velocity is v = (6.99 m/s)i + (3.66 m/s)j + (8.14 m/s)k and it is subject to a force F = (9.02 N)i – (3.34 N)j + (9.52 N)k. At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) j = (3.00 m), its velocity is = – (8.80 m/s) + (8.53 m/s) + (9.01 m/s) and it is subject to a force = (4.53 N) i – (2.58 N) j + (8.77 N) Find the acceleration of the object ( (a), (b) and (c) for and k components respectively), the angular
Physics For Scientists and Engineers 9th Edition Serway Test Bank | PDF | Force | Friction
Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) Step 1 The following information is given: m = 2 k g d → = 2 i ^ + 4 j ^ − 3 k ^ View the full answer Step 2 Step 3 Final answer Previous question Next question Transcribed image text: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is vec d =(2.00 m)hat i+(4.00 m)hat j-(3.00 m)hat k, its velocity is vec =-(6.00 m/s)hat i+(3.00 m/s)hat

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Addison Wesley Science 10 Unit B Solutions | PDF | Speed | Nuclear Fusion Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) Step 1 The following information is given: m = 2 k g d → = 2 i ^ + 4 j ^ − 3 k ^ View the full answer Step 2 Step 3 Final answer Previous question Next question Transcribed image text:

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Introduction to College Physics I: An Exploration of Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids, and Modern Physics | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Heat Solution Verified by Toppr Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1 The work done on an object does not depend on the : (a) displacement (b) angle between force and displacement (c) force applied (d) initial velocity of the object View Solution Q Refer question no 12 in the chapter 11.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
SOLVED: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d→ = (2.00 m) î + (4.00 m) ĵ – (3.00 m) k̂ , its velocity . Find (a) the acceleration of the object, (b) the angular momentum of the object about the origin, (c) the torque about the origin acting on the object, and (d) the angle between the velocity of the object and the force acting on the object. How do we benefit from the production of vitamin K by microbes?
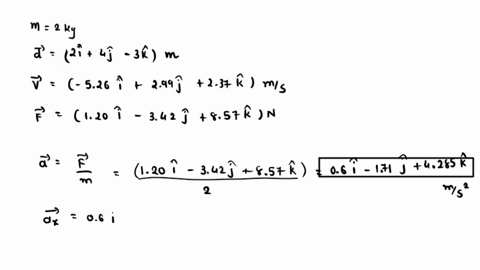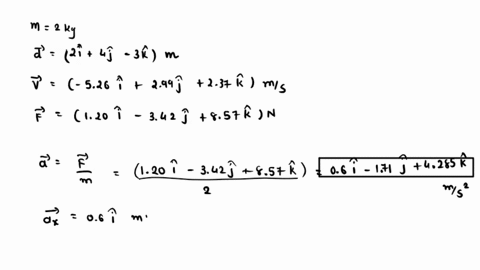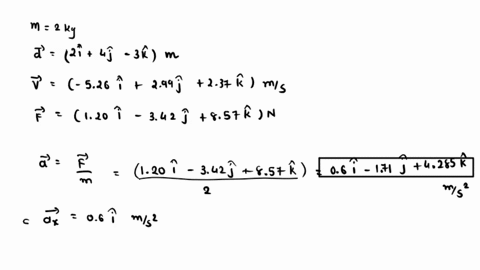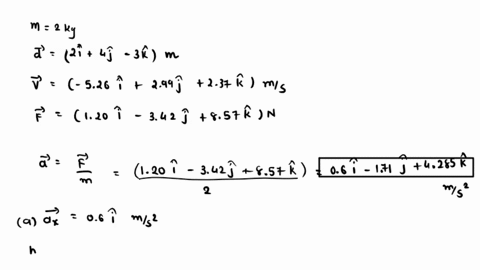
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Physics | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Trigonometry Textbook solution for Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition David Halliday Chapter 11 Problem 30P. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
General Physics Phys 1011 Module | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Significant Figures At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d = (2.00 m)i + (4.00 m)j – (3.00 m)k, its velocity is v = (6.99 m/s)i + (3.66 m/s)j + (8.14 m/s)k and it is subject to a force F = (9.02 N)i – (3.34 N)j + (9.52 N)k.

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Physics 12 | PDF | Force | Takeoff At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is = (2.00 m) + (4.00 m) j = (3.00 m), its velocity is = – (8.80 m/s) + (8.53 m/s) + (9.01 m/s) and it is subject to a force = (4.53 N) i – (2.58 N) j + (8.77 N) Find the acceleration of the object ( (a), (b) and (c) for and k components respectively), the angular

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
Addison Wesley Science 10 Unit B Solutions | PDF | Speed | Nuclear Fusion
Physics 12 | PDF | Force | Takeoff At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d = (2.00 m)i + (4.00 m)j – (3.00 m)k, its velocity is v = – (3.58 m/s)i + (6.72 m/s)j + (8.96 m/s)k and it
SOLVED: At the instant the displacement of a 2.00 kg object relative to the origin is d→ = (2.00 m) î + (4.00 m) ĵ – (3.00 m) k̂ , its velocity General Physics Phys 1011 Module | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Significant Figures Textbook solution for Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition David Halliday Chapter 11 Problem 30P. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!